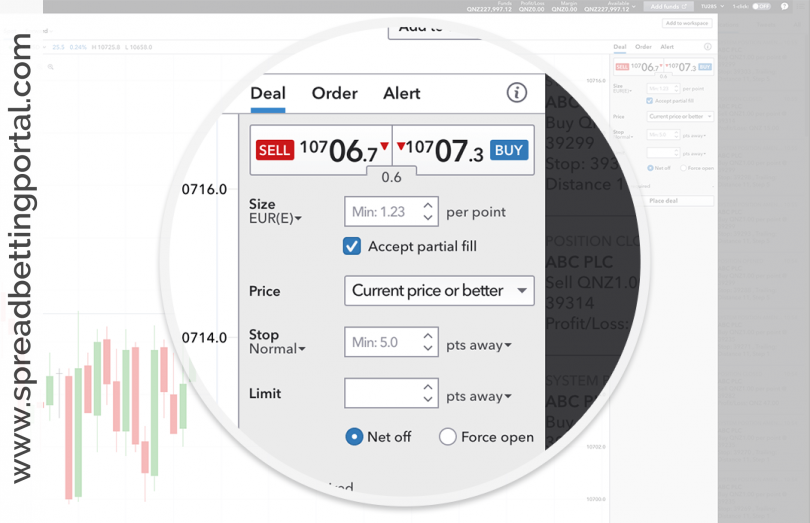
The best way to explain the mechanics of financial spread betting is probably by using trading examples and then comparing it to shares trading and traditional betting. For instance, if you placed a £10 fixed odds bet on a horse at 5-1 and your prediction proved correct (the horse wins), you would stand to win your original stake multiplied by the odds (£60). However, should your horse lose, then you would lose your original £60 stake.
Spread betting works differently in that you don’t have to predict the exact level of accuracy and the odds are not set in advance. The problem is that, handled carelessly it could result in sizable losses so it is important that beginners familiarise themselves with the trading product before diving in head-on. It is also wise to start small, and as always bet only with ‘risk money’. Investors who decide to use spread betting need to be very disciplined and respect stop losses; after all this is a leveraged product.
Give me an example…
Take the FTSE 100. If you place a bet at £25 per point and the FTSE rises by 10 points, you stand to make £250 (£25 x 20 points). But if it falls 50 points, you lose £500. The more the market you are betting on goes in your favour, the more you make; the more it moves against you, the more you lose.
In this respect financial spread betting works mainly by predicting the direction of a certain financial asset. Let’s take another example
Tom believes Barclays shares are going to rise in value. His spread betting providers is quoting 320p to buy and 319p to sell so he decides to buy at £30 per point. This gives him exposure to 3000 shares, equivalent to £9,600 of shares. Since the margin for Barclays is 10%, he deposits £960 to cover this trade.
If the price rises…
A few days later Barclays stock price has gone up to 342p to buy and 341 to sell, so Tom sells at 341p. The price has increased 21 points so at £30 a point, this translates into a profit of £630. With this, Tom also gets his £960 margin deposit back minus any financing interest that has been accrued during this period.
If the price falls
A few days later Barclays’ price falls to 301p to buy and 300p to sell, so Jonathan decides to cut his losses and sell at 300p. The price has fallen by 19 points so at £30 per point he has suffered a loss of £380. This, plus any financing charges, is deducted from his £960 margin deposit.
Let’s now take an index spreadbet example. For instance, say you reckon that the FTSE 100 is likely to go up. The FTSE 100 is currently being quoted at 5,545 and you are quoted a spread of 5,544-5,546 by your spread betting firm. In this instance you could ‘buy’ or ‘go long’ the FTSE by buying a certain amount per point at 5,546. Let’s suppose you bet £20. If your prediction proves to be correct and the FTSE 100 does rise to 5,590. you would make [(5590-5546) x £20 = £880. However, in the circumstance that you were wrong and the FTSE actually dropped to 5,520, you would then have lost £520.

In our trading guide, we look at how you can spread bet European indices – such as the FTSE 100, CAC 40 and DAX 30 – with real-life examples
Plan & Strategise: Spread Betting the DAX 30
Let’s suppose that you plan to open a long position and buy the DAX 30 index – commonly referred to as the Germany 30 DFT with most spread betting companies – for a stake of £10 per point.
You wish to limit your maximum loss to £150 and thus place a stop loss 15 points below the buy price.
Trade: Go Long on the DAX 30
You enter a long position and buy the Germany 30 DFT based on positive news coming out of the Eurozone. Since you have opened a long position, if the DAX 30 moves in your favour and rises, you will net a gain every point that the index goes up.
However, should your prediction turn out to be wrong and the market moves against you, you will suffer a loss for every point it goes down. This is why stops are so important when spread betting the financial markets.
However, should your prediction turn out to be wrong and the market moves against you, you will suffer a loss for every point it goes down. This is why stops are so important when spread betting the financial markets.
When spread betting, investors would do well to use a trading strategy that could be based on pricing, fundamentals or even risk exposure. Traders need also have established entry and exit criteria in advance.